Welcome
Texas Hearing Clinic is proud to offer a full diagnostics suite in our San Marcos, TX. Below you can learn about the three primary vestibular diagnostic services available at Texas Hearing Clinics and get answers to frequently asked questions.
|
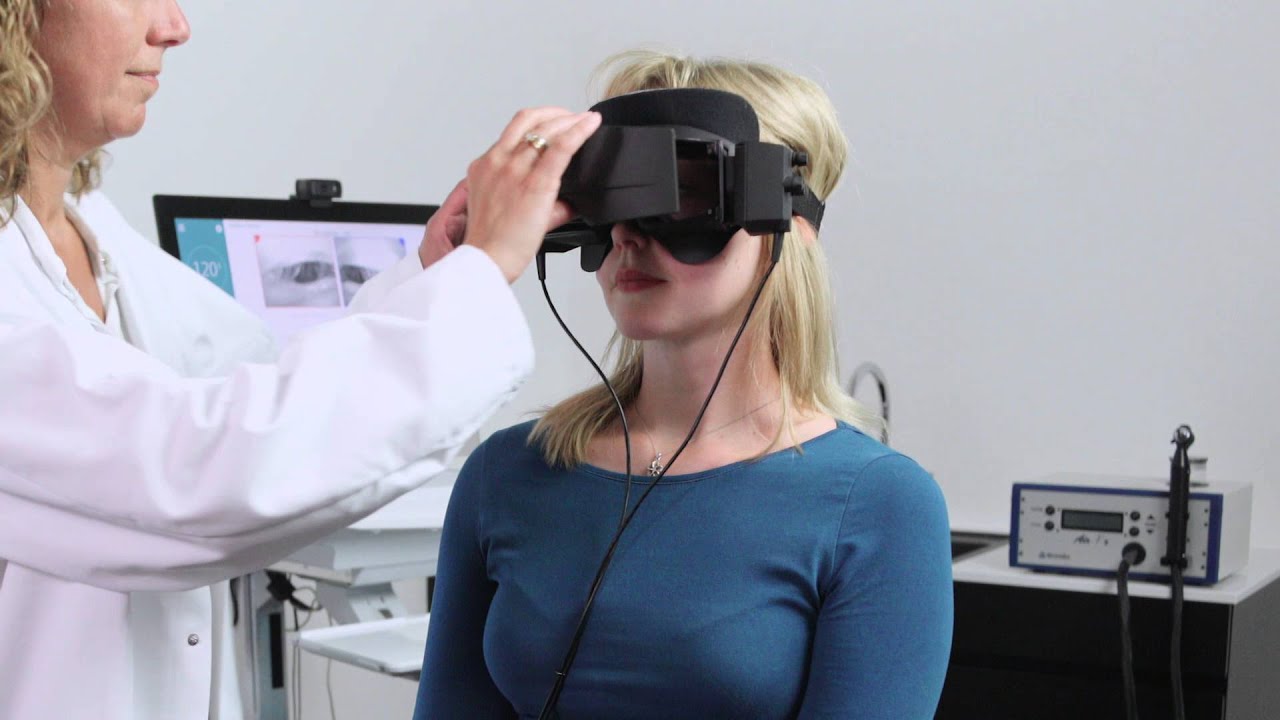
The Videonystagmography (VNG) is a technology for testing inner ear and central motor functions, a process known as vestibular assessment. It involves the use of infrared goggles to trace eye movements during visual stimulation and positional changes.
When we evaluate your vestibular system using the VNG equipment, we are assessing your overall oculomotor function, your response to positions (certain vestibular disorders flare up when you are in a certain position), and using air calorics (which evaluates the lateral semicircular canal response). |
The Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. The ABR can assess if there is retrocochlear neural dysfunction in one ear or the other which may be affecting your vestibular system.
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potential (VEMP) can test the utricle and saccule vestibular structure health. |
The Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) is a measure of the patient's vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) in response to head movement. A patient with a healthy vestibular system should be able to keep his/her eyes focused on a stationary target, even if the head is in motion.
In patients with vestibular dysfunction, when the head moves; the eyes will move with the head, requiring a corrective movement back to the target (this is known as "catch-up saccade"). This test helps us to determine the health and function of all the the semicircular canals, rather than just the lateral semicircular canals. The posterior and anterior semicircular canals would be missed in the VNG testing. |
Where is the nearest balance center?
Directions to our Balance Clinic can be found here.
Directions to our Balance Clinic can be found here.
Do I have to complete any paperwork?
To expedite the process, you can complete the following forms before your appointment. Please also bring your identification and insurance card(s).
To expedite the process, you can complete the following forms before your appointment. Please also bring your identification and insurance card(s).
What can I expect?
When you come in for a balance evaluation in our clinic, it is due to your physician wanting to rule out whether your vestibular system is impacting your current symptoms. If you are having vertigo (a spinning sensation) or have been experiencing the inability to move due to falling, it is essential to be evaluated by your primary care provider. There can be many factors affecting your ability to maintain equilibrium.
An audiologist is a key team player in the diagnosis of balance disorders. Once the primary care provider has ruled out your medication, heart health, and overall health and well being being a contributor to your balance problems, they may send you to Audiology to rule out the vestibular system.
We will conduct a hearing and balance assessment to determine whether your inner ear balance organs are impacting your equilibrium issues. This includes a standard hearing test, a videonystagmography test, and calorics.
Videonystagmography consists of wearing a set of goggles with an attached infrared camera that tracks the pupil movement. We will do multiple tests including eye movement tasks, body positioning tasks, then an air calorics test. This Air Caloric test includes cool and warm air being directed into each ear separately with a recording of your eye movement during this stimulus. This test may cause some vertigo, but it should not last more than 3 minutes after the testing is completed.
When you come in for a balance evaluation in our clinic, it is due to your physician wanting to rule out whether your vestibular system is impacting your current symptoms. If you are having vertigo (a spinning sensation) or have been experiencing the inability to move due to falling, it is essential to be evaluated by your primary care provider. There can be many factors affecting your ability to maintain equilibrium.
An audiologist is a key team player in the diagnosis of balance disorders. Once the primary care provider has ruled out your medication, heart health, and overall health and well being being a contributor to your balance problems, they may send you to Audiology to rule out the vestibular system.
We will conduct a hearing and balance assessment to determine whether your inner ear balance organs are impacting your equilibrium issues. This includes a standard hearing test, a videonystagmography test, and calorics.
Videonystagmography consists of wearing a set of goggles with an attached infrared camera that tracks the pupil movement. We will do multiple tests including eye movement tasks, body positioning tasks, then an air calorics test. This Air Caloric test includes cool and warm air being directed into each ear separately with a recording of your eye movement during this stimulus. This test may cause some vertigo, but it should not last more than 3 minutes after the testing is completed.
We are here to help.
We know that you are suffering when you are dealing with vertigo and imbalance. These symptoms can stop enjoyment of life when you are experiencing them. Our goal is to help your physician move quickly on diagnosis and treatment. Due to this, we will send our results the same day to your physician to help him/her assess your overall symptoms.
We know that you are suffering when you are dealing with vertigo and imbalance. These symptoms can stop enjoyment of life when you are experiencing them. Our goal is to help your physician move quickly on diagnosis and treatment. Due to this, we will send our results the same day to your physician to help him/her assess your overall symptoms.
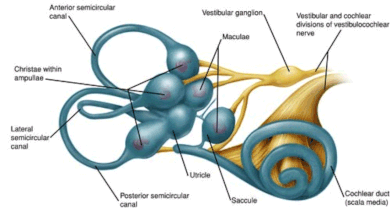
How does the vestibular system impact my balance?
The vestibular system is one of many parts of our balance system. We use our vision, the feeling in our feet (proprioception), and our vestibular system to sense movement in our environment and on our body. When something goes wrong with any of these or with our cardiac or brain health, we can experience dizziness and imbalance.
The vestibular system is made up of 5 different sensory organs in the inner ear that sense our movement in relation to gravity. These are the anterior semicircular canal, posterior semicircular canal, lateral semicircular canal, utricle, and saccule. If one of these systems is not working appropriately, or if there is something impacting the 8th cranial nerve, our brain receives a mismatch in the information from our vestibular system and our visual and proprioceptive system.
The audiologist will go through a complete hearing and balance assessment should this be requested by your physician. This will rule out the vestibular system as the reason for your inequilibrium.
If you are scheduling an appointment for a balance assessment, call us and complete the balance evaluation form to bring in to your appointment.
The vestibular system is one of many parts of our balance system. We use our vision, the feeling in our feet (proprioception), and our vestibular system to sense movement in our environment and on our body. When something goes wrong with any of these or with our cardiac or brain health, we can experience dizziness and imbalance.
The vestibular system is made up of 5 different sensory organs in the inner ear that sense our movement in relation to gravity. These are the anterior semicircular canal, posterior semicircular canal, lateral semicircular canal, utricle, and saccule. If one of these systems is not working appropriately, or if there is something impacting the 8th cranial nerve, our brain receives a mismatch in the information from our vestibular system and our visual and proprioceptive system.
The audiologist will go through a complete hearing and balance assessment should this be requested by your physician. This will rule out the vestibular system as the reason for your inequilibrium.
If you are scheduling an appointment for a balance assessment, call us and complete the balance evaluation form to bring in to your appointment.